Non-Destructive Testing
Non-destructive testing (NDT) provides critical field data to help identify visible and hidden conditions within reinforced concrete structures, supporting condition assessments without invasive investigation.
NDT Corporation provides non-destructive testing services to evaluate concrete durability, locate internal defects, and detect corrosion-related deterioration. Our skilled technicians work with engineers and asset owners to identify the appropriate testing technologies for each project and deliver accurate, quantitative datasets that support structural assessments, repair design, rehabilitation planning, and long-term asset management.
METHODS
Acoustic Tomography
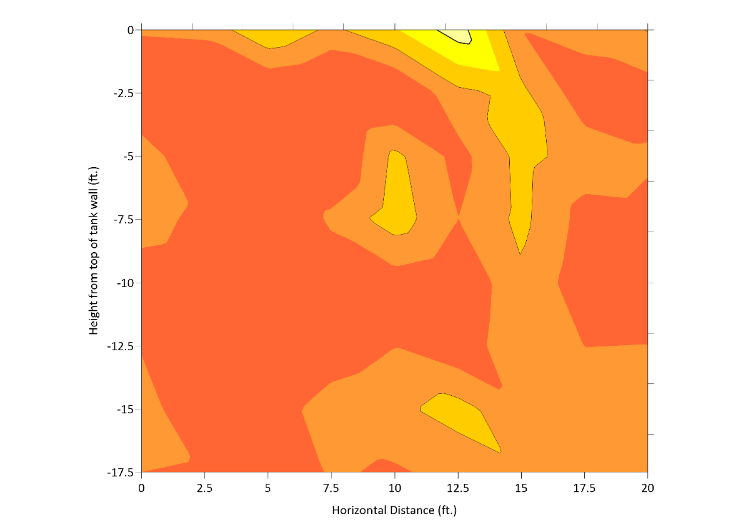
Acoustic Tomography is used to evaluate reinforced concrete elements and identify internal defects, such as voids, cracking, honeycombing, and low-strength concrete, that cannot be detected through visual inspection alone.
This method supports concrete condition assessments by helping engineers understand subsurface anomalies that may impact structural performance or durability.
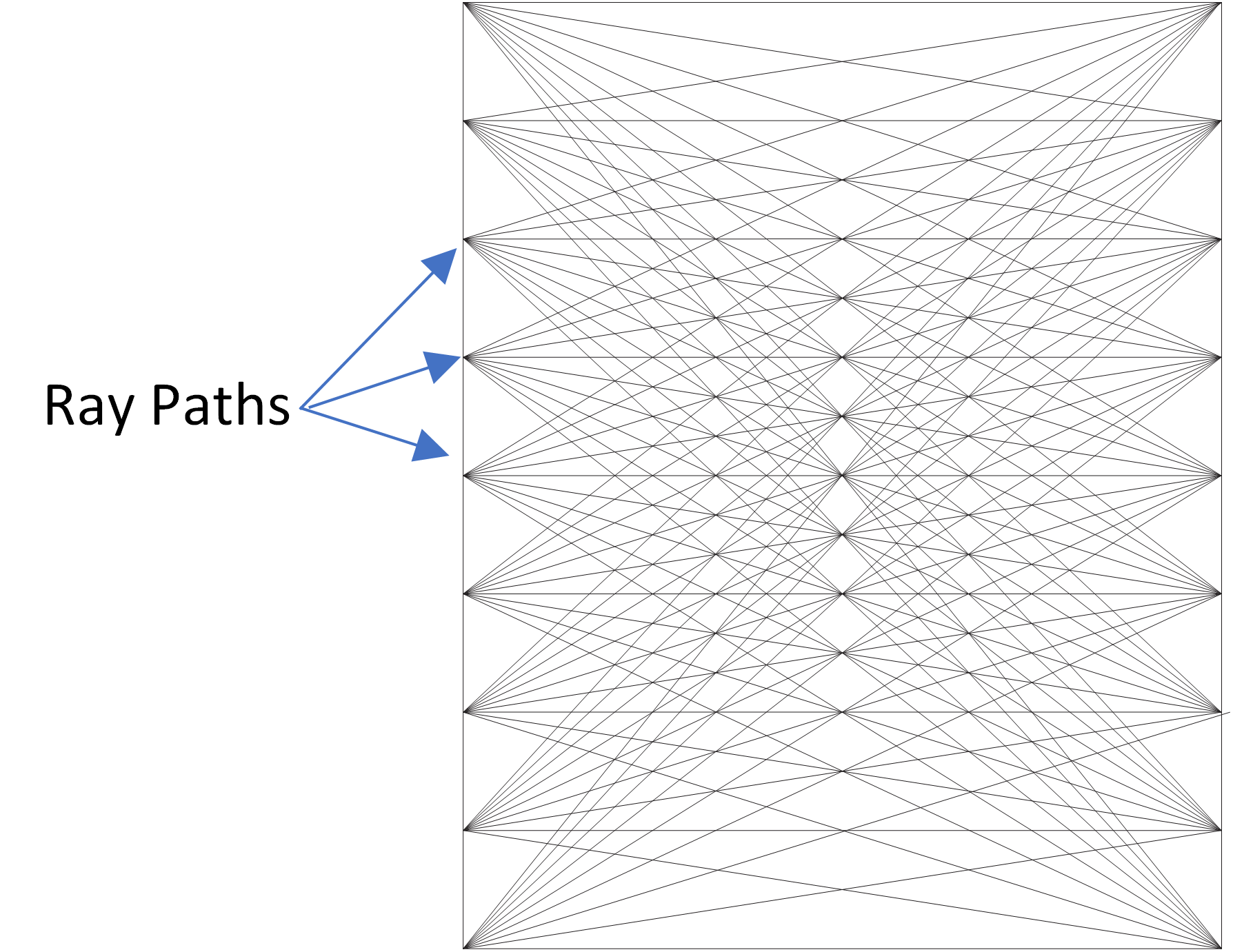
During testing, acoustic transmitters and receivers are placed on opposing sides of the concrete member. Compressional wave velocity is measured as the signal passes through the material. These measurements are collected across a dense survey grid and compiled into 2D and 3D models, producing detailed images of wave velocities throughout the structure. Zones exhibiting lower-than-average velocities may indicate internal deterioration, such as fractures, cracking, honeycombing, low-strength concrete, or voids.
Acoustic tomography may also be used for quality assurance and quality control (QA/QC) of concrete repairs. Following remediation, testing can be repeated to confirm that identified voids or honeycombing have been effectively addressed, helping verify repair completeness before structures are returned to service.
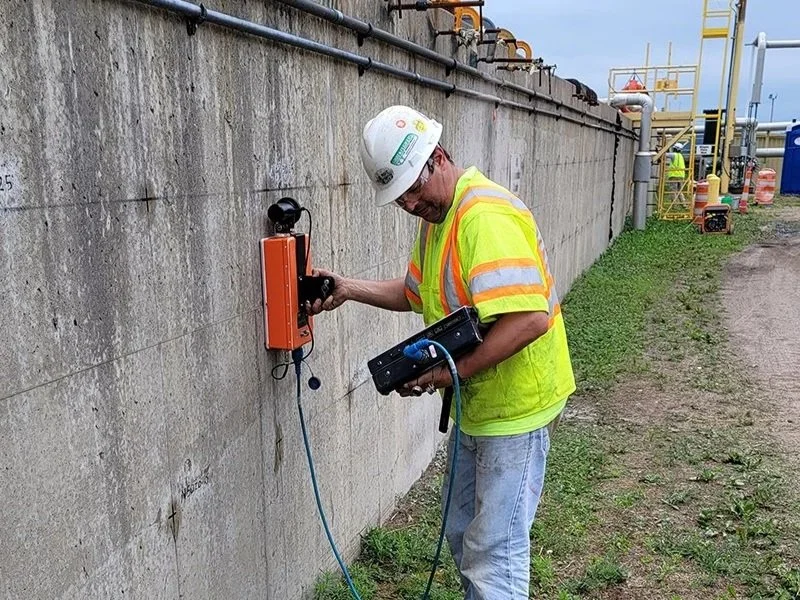
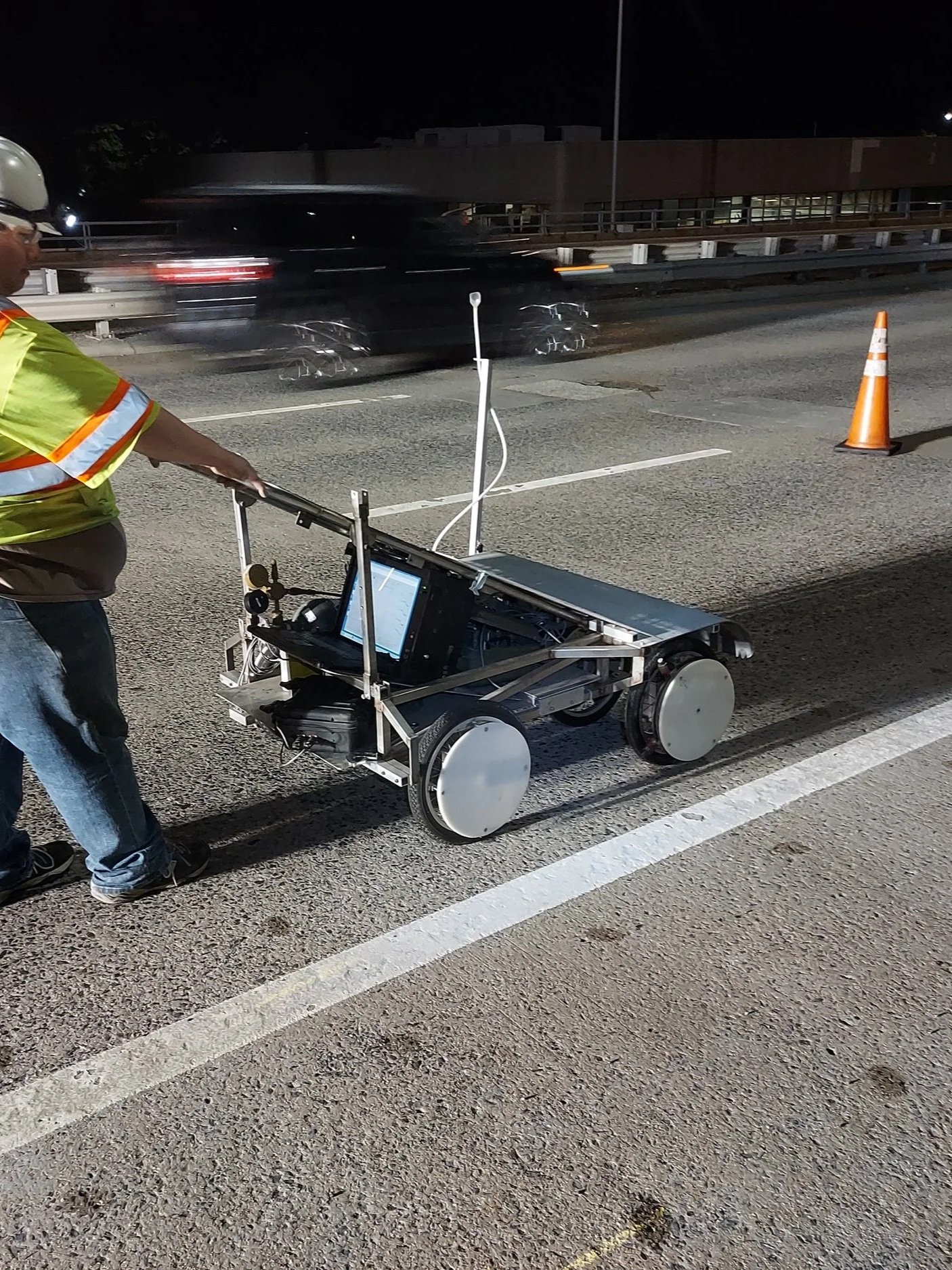
Ground penetrating radar (GPR) is used to locate embedded steel reinforcement and measure cover depth within concrete elements. The method collects subsurface data used to identify changes in material response associated with reinforced concrete conditions.
GPR is a rapid, cost-effective, non-invasive testing technique that enables efficient scanning of large areas. The data supports evaluations of existing structures and provides insight into as-built conditions when drawings or records are limited.
In addition to concrete structures, GPR is commonly used to determine pavement thickness and identify layering within roadway systems.
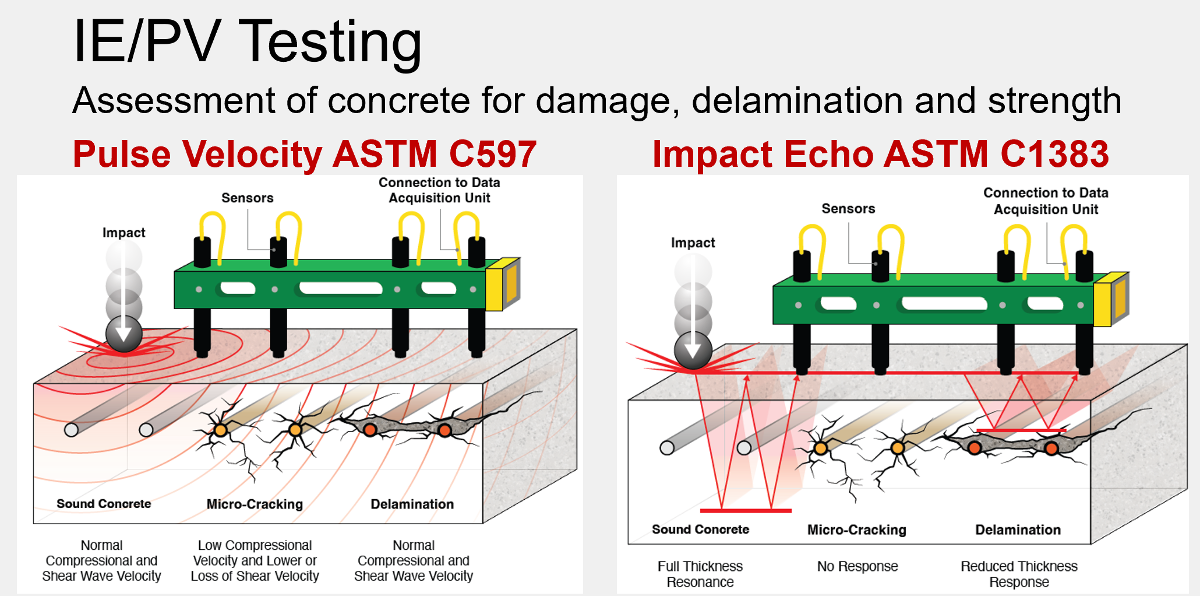
Impact echo / pulse velocity (IE/PV) is a non-destructive testing method that introduces stress waves into concrete and measures their response to evaluate material properties and identify internal defects such as delamination, cracking, voids, and honeycombing.
NDT Corporation uses a custom IE/PV system that simultaneously collects impact echo and pulse velocity data, improving testing efficiency during structural assessments. IE/PV testing can also be used to estimate in-situ concrete compressive strength and evaluate internal concrete quality.
Corrosion Potential Mapping
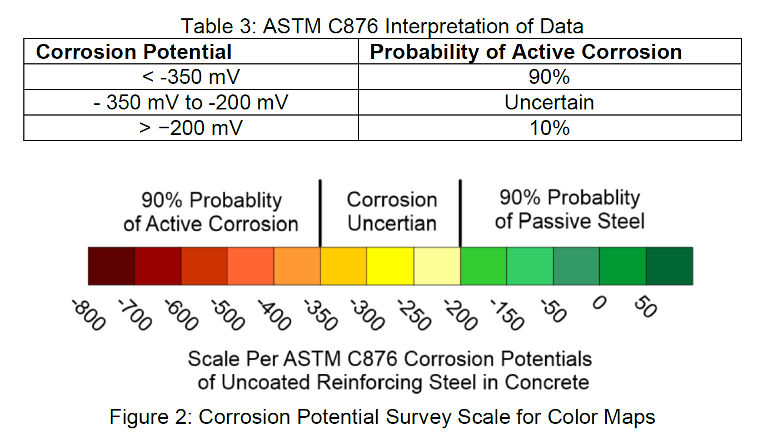
Our team collects corrosion potential measurements to evaluate the likelihood of corrosion in embedded reinforcing steel and submerged steel structures. Measurements are taken across multiple locations to capture potential differences across the structure.
The results are compiled into a corrosion potential map that illustrate areas of higher and lower corrosion risk. These measurements provide engineers with critical data when evaluating global versus targeted corrosion mitigation strategies.
Ground Penetrating Radar
Impact Echo / Pulse Velocity
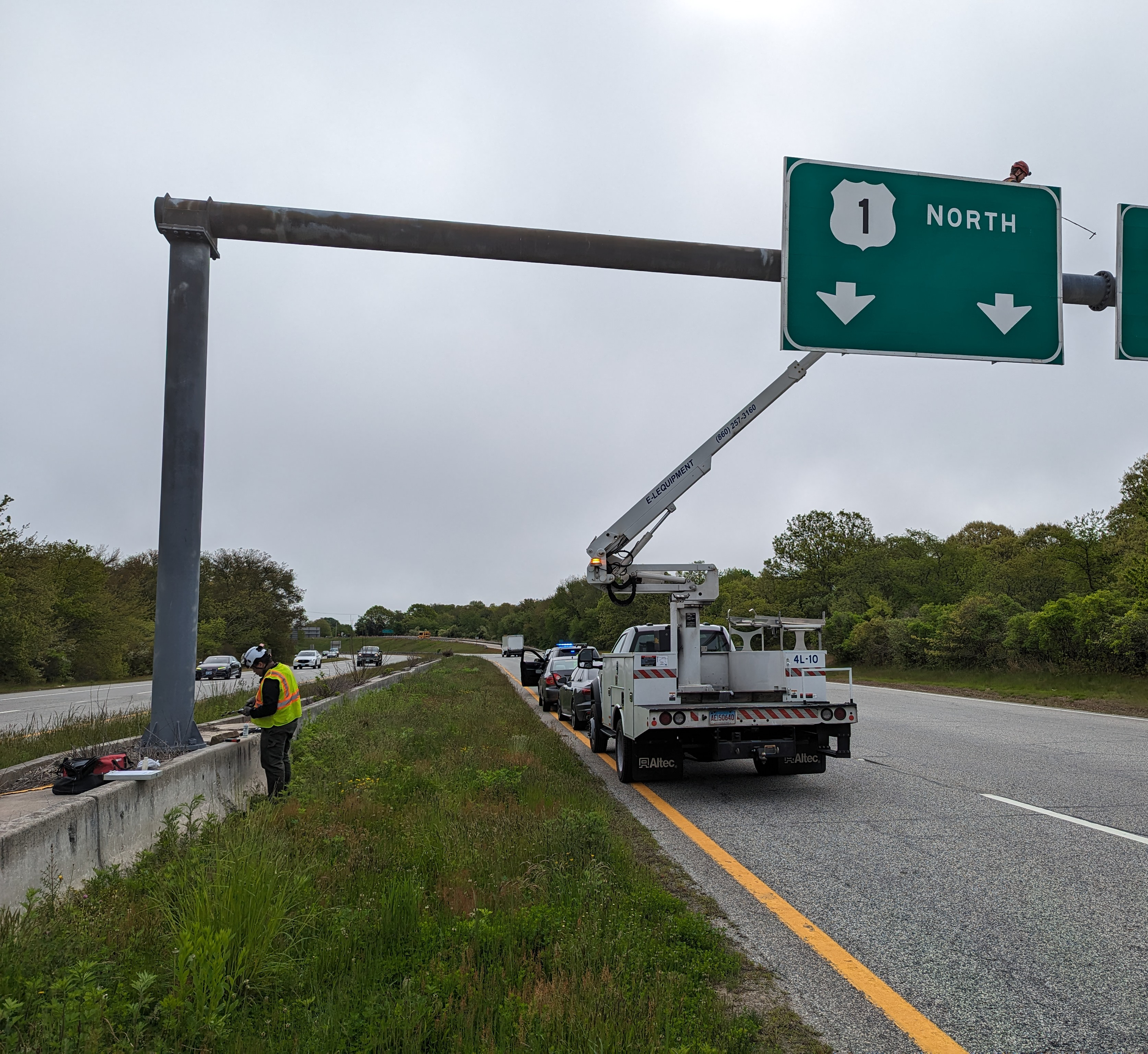
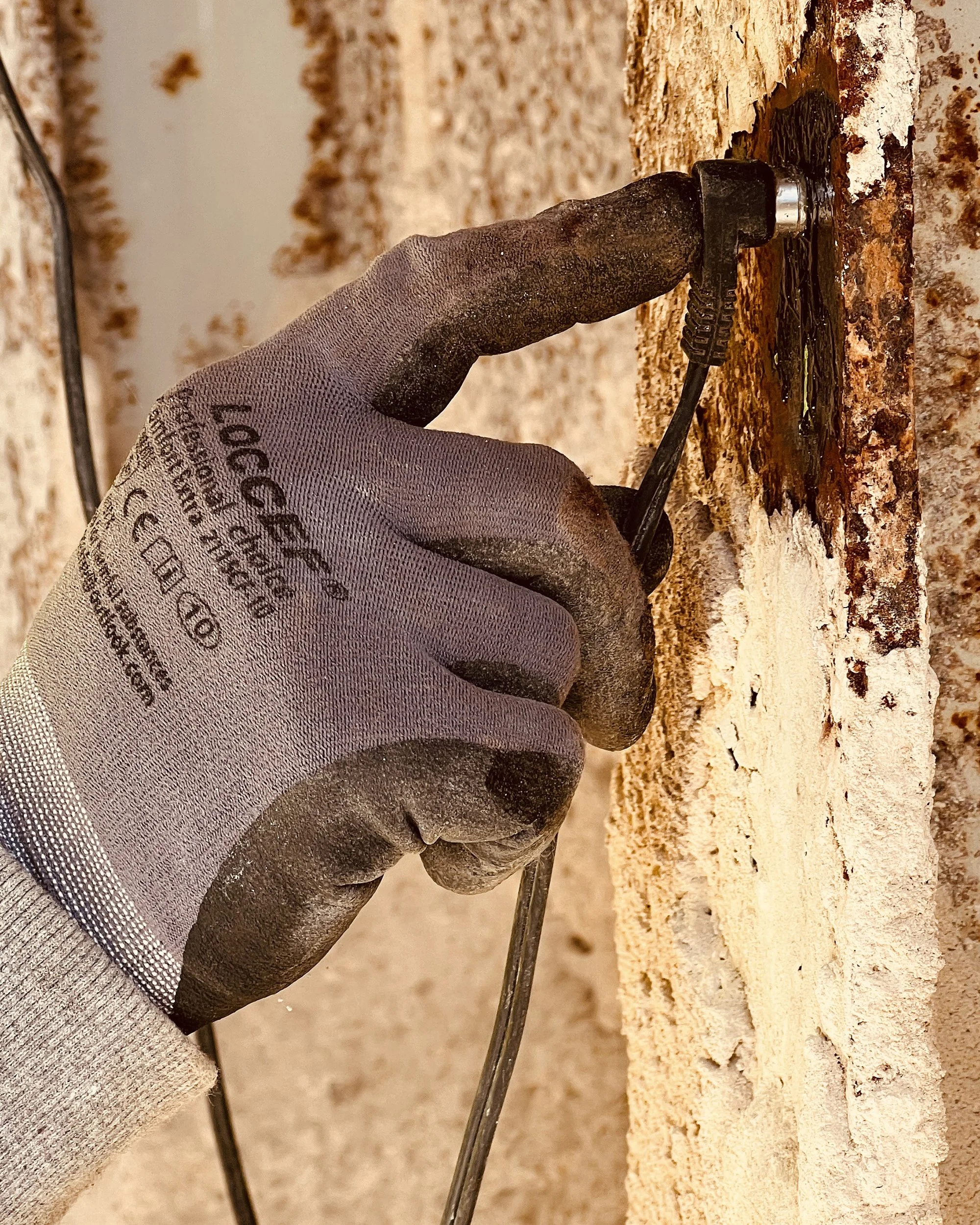
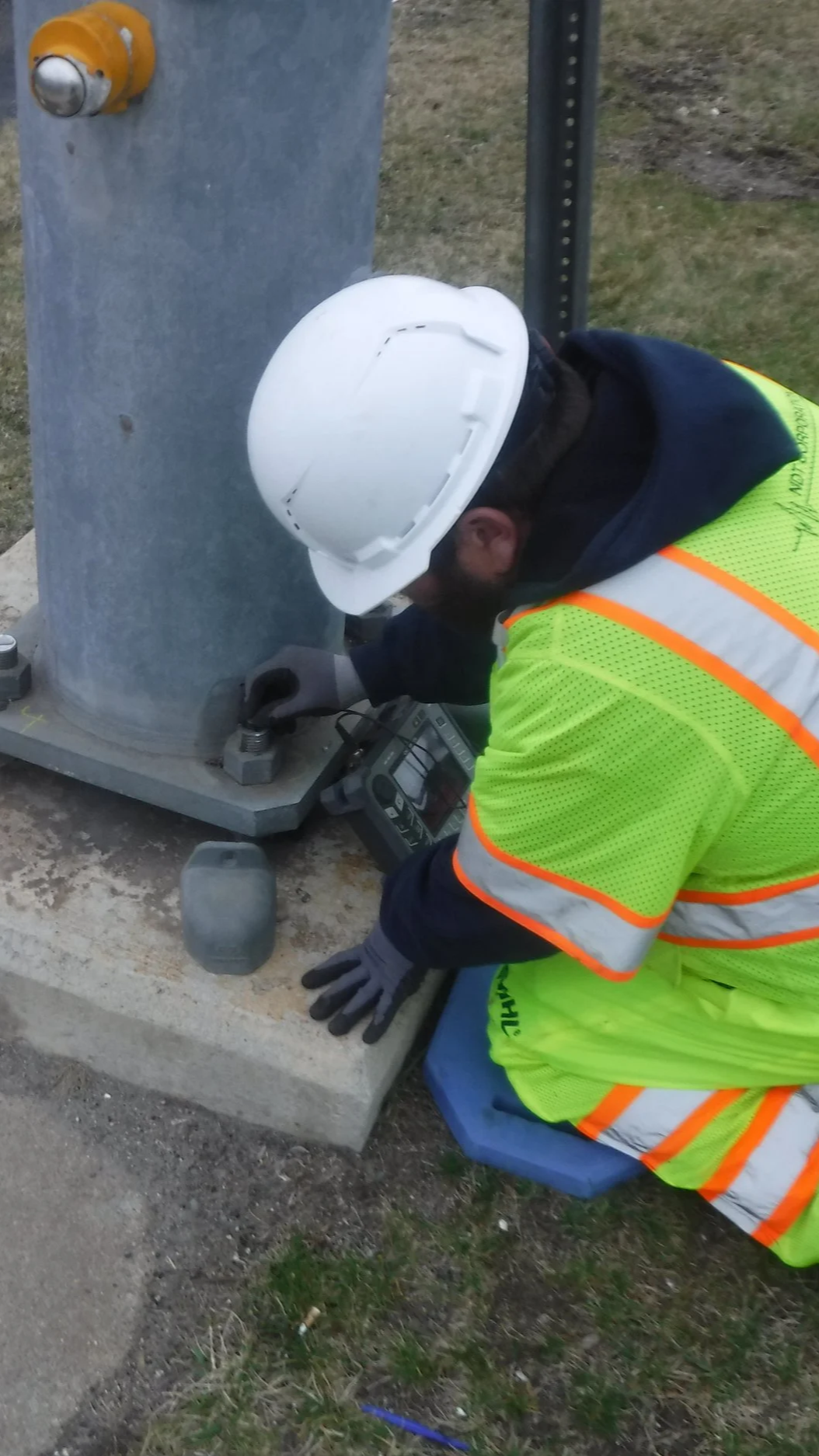
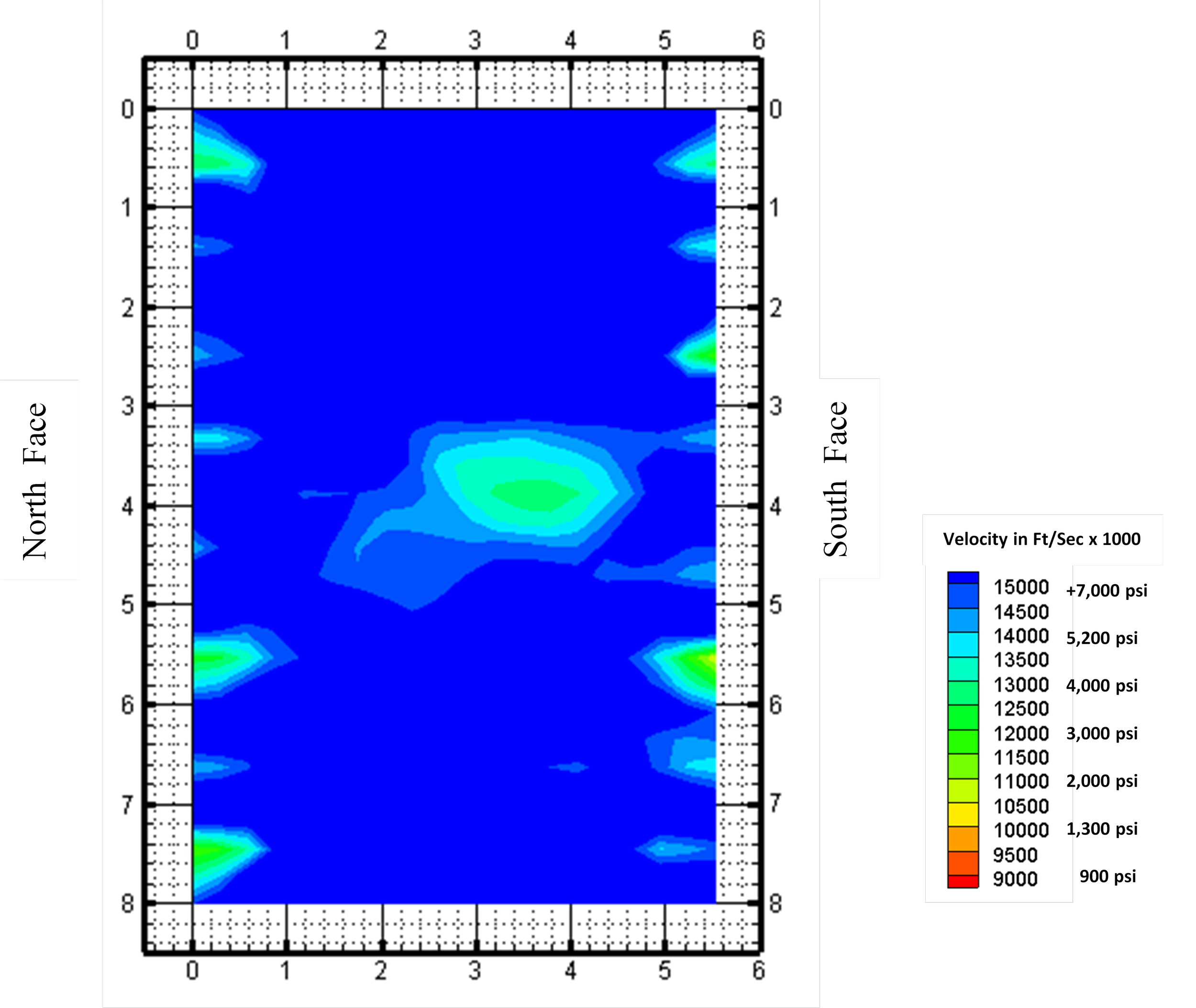
Ultrasonic thickness (UT) testing is used to measure the thickness of steel components by transmitting a high-frequency ultrasonic signal through the material and recording the signal’s travel time. The measured response is used to calculate the remaining thickness of steel elements.
UT measurements can be collected to document section loss in steel affected by corrosion. When combined with known information such as original member thickness and structure age, the data may be used by project teams to quantify material loss over time.
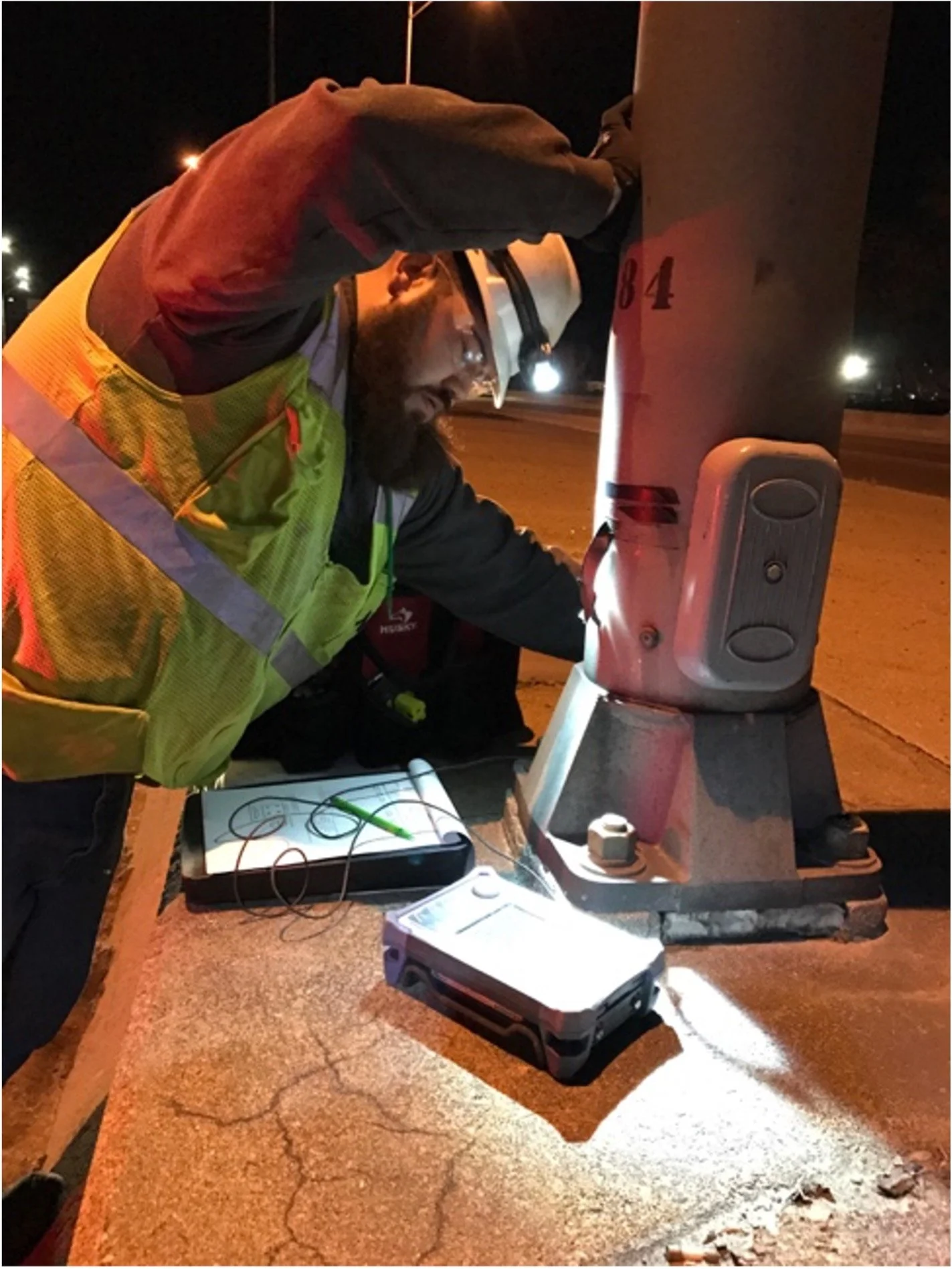
In addition, NDT Corporation uses UT to measure the length of bolts and if there are any cracks, flaws, or fractures along their length. NDT Corporation commonly performs UT on anchor bolts associated with roadway signs, traffic signals and light pole foundations to confirm their condition, as these elements have been known to corrode, leading to signage failures that lead to the signs crashing down into the roadway.
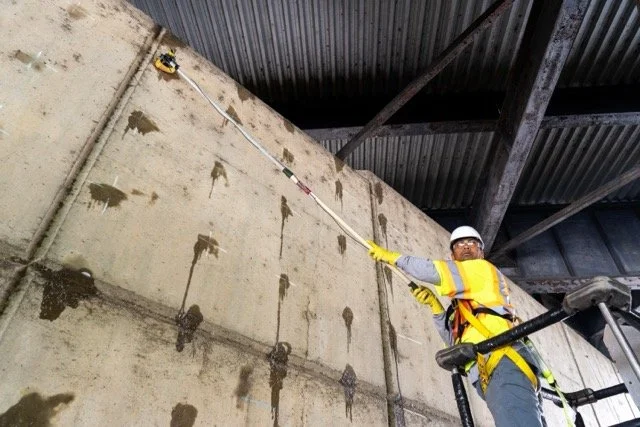
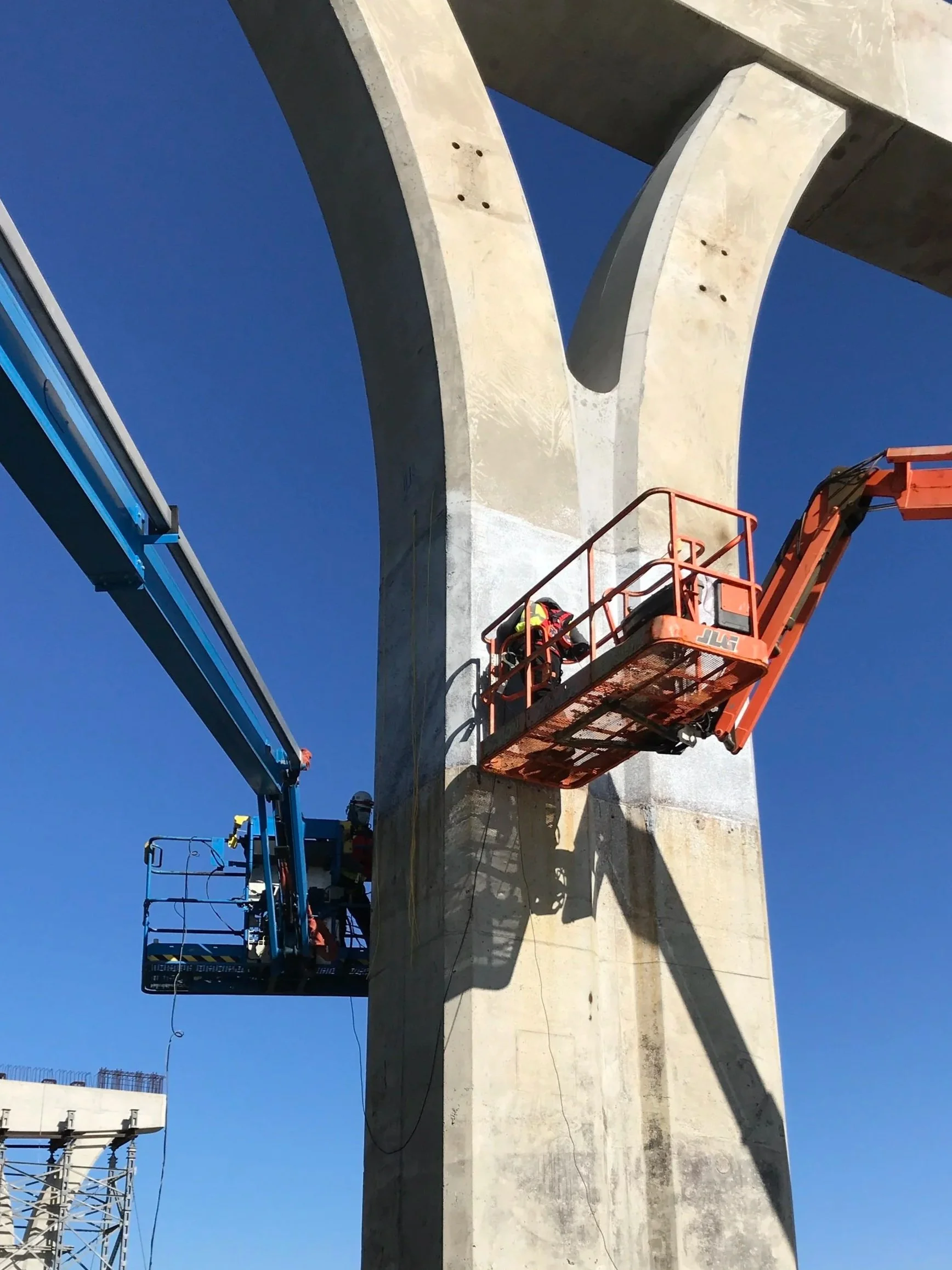
Performing through testing on a bridge column.
IR results showing the progression of heat absorption at different time intervals. Results reveal a hidden anomalies within the concrete.
IE/PV deck tester collecting data on a bridge deck.
Applications of IE/PV
IE/PV Deck Tester
For more than 20 years, NDT Corporation has used a bridge deck testing system developed in collaboration with Departments of Transportation. This system is routinely deployed on bridge decks and slabs to efficiently collect IE/PV data that supports concrete condition assessments.
Surface Testing vs. Through Testing
IE/PV data may be collected using surface testing, where the energy source and sensors are positioned adjacent to one another on the same face of the concrete. When access is available on both sides of a member, through testing can be performed with the energy source and sensors placed on opposite faces.
Through testing may also be used to assess consolidation issues in cast-in-place concrete. Conditions such as honeycombing and cold joints can affect durability and reduce concrete strength relative to design expectations.
Infrared Thermography
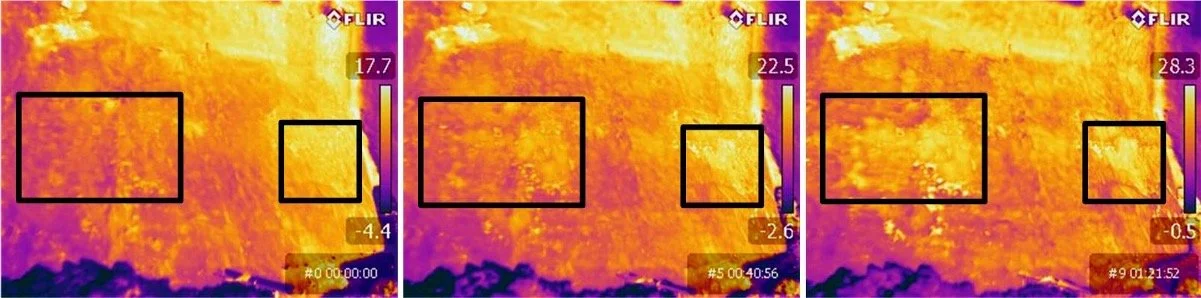
We use Infrared Thermography (IR) to identify delaminated concrete over a large area in a short period of time. When concrete is exposed to solar heating, areas containing delamination’s tend to warm and cool at different rates than intact concrete.
These temperature differences can be captured using an infrared camera and displayed as a thermal image. The resulting images provide a visual representation or assessment of potential delamination’s useful for estimating overall repair quantities.
Large near-surface delamination’s are more easily identified as IR is comparable to a hammer-sounding survey.
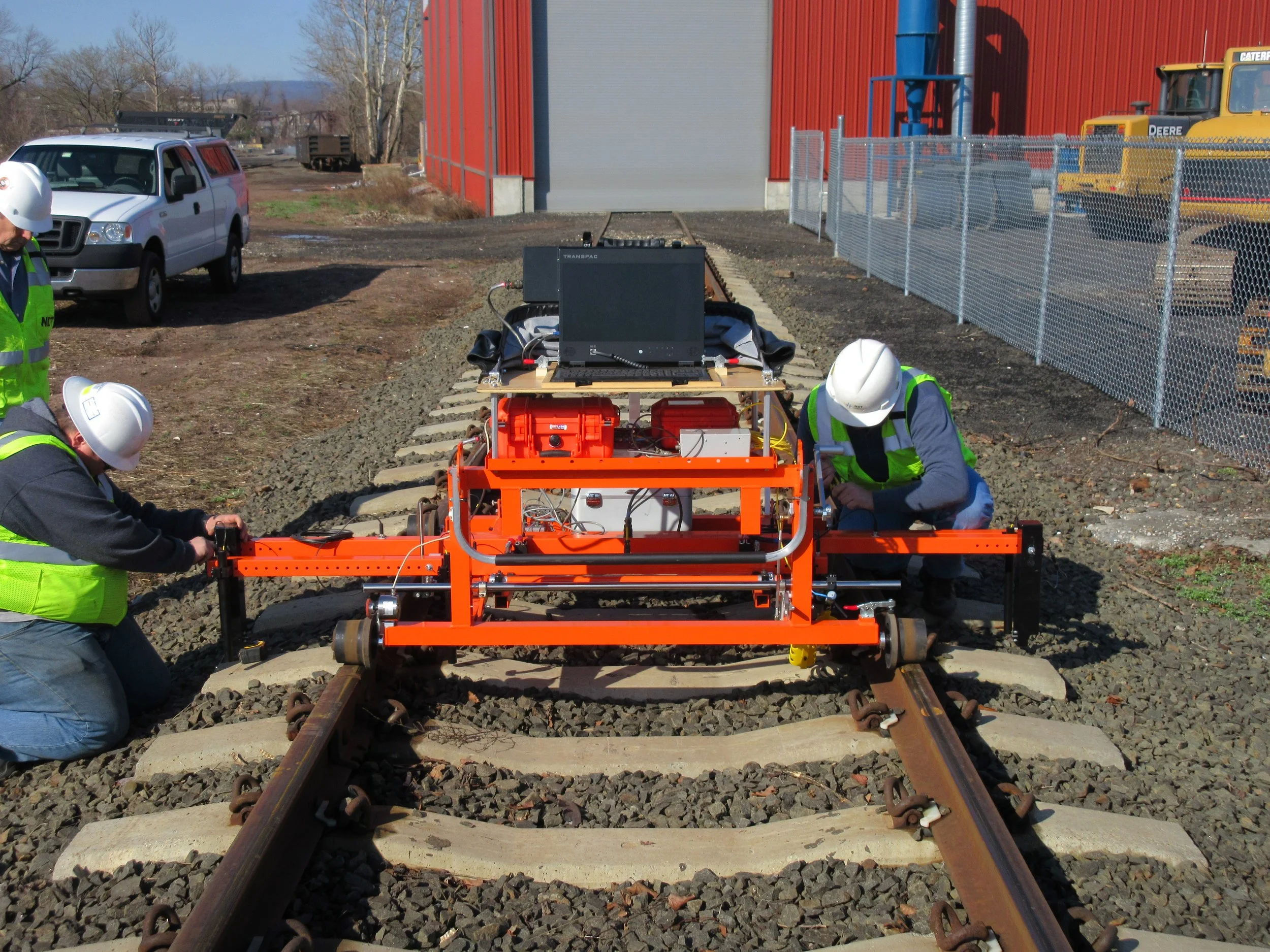
Railroad Tie Testing
Concrete crossties are crucial for global rail networks, ensuring safe freight and passenger operations. Assessing each crosstie's condition is vital for rail transit safety.
Traditional visual inspections, whether by personnel or high-speed imaging, only evaluate external conditions, overlooking internal deterioration that precedes surface damage as visible damage is already severe when observed.
NDT addresses this with the Automated Concrete Tie Tester (ACTT) system, utilizing non-destructive pulse velocity (PV) evaluation. The ACTT provides real-time ratings (1-5) based on internal conditions, automating maintenance decisions for crossties with severe damage (4 and 5 ratings).
Ultrasonic Thickness (UT) Testing
Experience You Can Rely On
Since 1994, NDT has built a reputation for delivering reliable data, practical insight, and responsive service on technically complex projects. Our team combines decades of field experience with advanced testing technologies to produce results that are clear, defensible, and actionable for engineers and owners.