Geophysics, Subsurface & Pile Testing
NDT Corporation applies advanced geophysical and subsurface testing methods, supported by state-of-the-art equipment to provide valuable data on subsurface conditions. This allows our clients to make informed decisions and reduce the chance of costly issues.
Testing services may include identifying unknown foundations or subsurface features, as well as documenting soil layering and material composition. NDT Corporation’s role is focused on data collection and measurement, providing objective results that can be used by owners, engineers, and consultants in their project planning and decision-making processes. All testing is performed in accordance with applicable standards and regulatory requirements.
NDT Corporation is committed to delivering high-quality testing services with a strong emphasis on accuracy, consistency, and attention to detail. Each project is approached with care to ensure data is collected efficiently and documented clearly, supporting the needs and objectives of the project team.
METHODS
Cross-Hole Compressional and Shear Wave Measurements
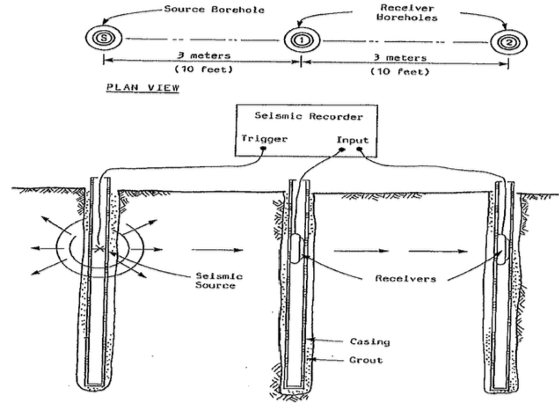
Cross-hole testing is used to evaluate soil conditions between multiple boreholes using a cross-hole seismic methodology. Seismic compressional and shear wave velocities are measured as waves travel through the soil from one borehole to another.
The recorded wave velocity data is used to classify subsurface materials based on their mechanical properties. These measurements are compiled into a velocity profile that identifies higher- and lower-velocity soil layers.
Because wave paths cross between boreholes, the data can also be used to detect horizontal and vertical variations in subsurface conditions. Localized high- or low-velocity zones may indicate discontinuities or changes within the soil strata.
Electrical Resistivity
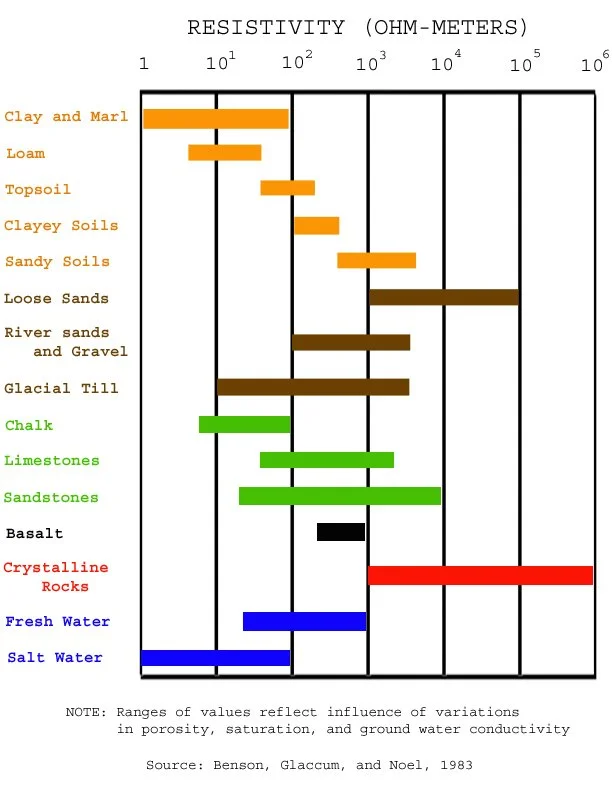
Electrical resistivity testing of soils is used to identify areas where elevated moisture infiltration or potentially corrosive soil conditions may be present. Zones exhibiting lower resistivity values are typically associated with environments that are more conducive to corrosion activity.
Because moisture content has a significant influence on resistivity, these measurements can also be used to locate seepage within soils and earthen structures. One key application of soil resistivity testing is identifying potential leakage paths beneath earthen dams, dikes, and concrete spillways.
Seepage beneath these structures produces localized low-resistivity zones that can be detected through resistivity testing. In addition, resistivity measurements can be used to identify subsurface features such as sinkholes.
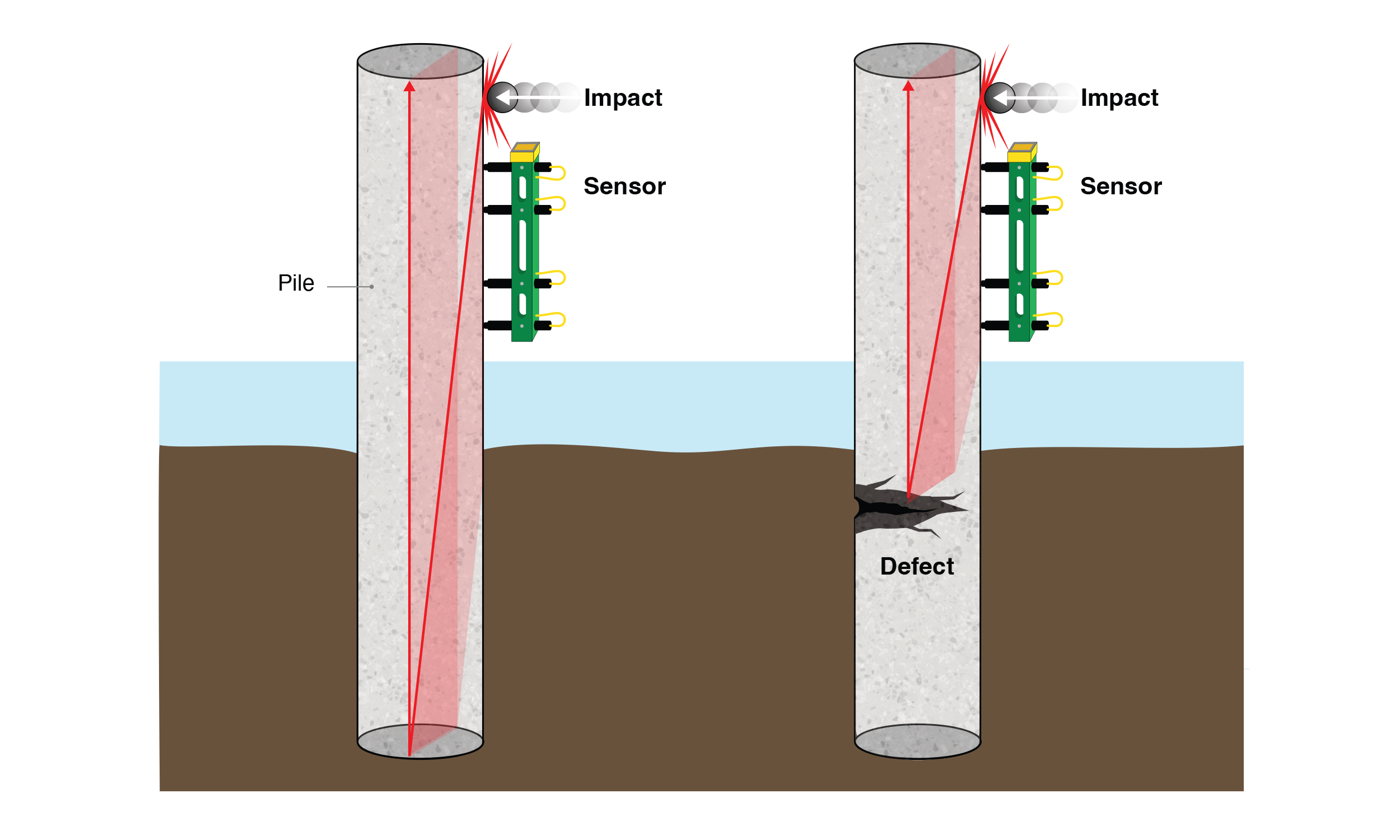
Pile length testing is used to determine the length of steel, timber, and concrete piles using the Pile Integrity Test (PIT) method.
PIT is also commonly referred to as sonic integrity testing, sonic reflection, or sonic echo testing. PIT also a lateral deflection component and load capacity. NDT Corporation provides the length data for timber, steel and concrete piles.
The method works by applying a small hammer impact at the top of the pile and measuring the time it takes for the resulting stress wave to travel to the bottom of the pile and return to the surface. Based on this travel time, the length of the pile can be determined.
PIT testing can also identify significant changes along the pile length that may indicate damage or other internal defects.
Seismic Refraction and Reflection
Seismic refraction and reflection surveys use compressional wave measurements to examine subsurface conditions. These surveys are used to identify different material types, estimate layer thicknesses, and map the top of bedrock beneath the ground surface.
The collected data is used to determine soil layer depths and wave velocities, which provide information about soil composition and subsurface structure.
At NDT Corporation, we process the data and create a profile of the various soil layers and bedrock, including thicknesses obtained from the compressional wave velocities for each layer.
Parallel Seismic Data
Parallel seismic testing involves collecting seismic data using a borehole placed next to a pile. During testing, a signal is generated at the top of the pile, and the pile itself is used to carry that signal downward.
The time it takes for the signal to travel from the top of the pile to its base is measured. Because the signal travels faster through the pile than through the surrounding soil, measurements recorded in the nearby borehole can be used to identify the depth of the pile and locate the pile tip.
Pile Length Testing – Sonic Echo
Vertical Seismic Profiling (VSP)
Vertical seismic profiling (VSP) uses compressional and shear wave measurements to collect information about soil and bedrock conditions. The method involves placing a sensor inside a single borehole while seismic energy is generated at multiple locations on the ground surface.
By recording how the seismic waves travel from the surface to the sensor, VSP testing provides data on compressional and shear wave velocities within the soil and bedrock layers. These measurements help document changes in subsurface conditions with depth.
Experience You Can Rely On
Founded in 1994, NDT has built a reputation for delivering reliable data, practical insight, and responsive service on technically complex projects. Our team combines decades of field experience with advanced testing technologies to produce results that are clear, defensible, and actionable for engineers and owners.